It is a method for joining metal pieces by heating them up to where they melt together and form a bond. The welding process is used in many mechanical devices to strengthen them than before. Various welding processes use electric current, an oxyacetylene torch, or a laser to create enough heat to melt the metal. Some welding methods require the addition of pre-made electrodes or foil filled with filler material while others do not require the addition of any materials at all. Throughout the following article, we will discuss the various welding types and how they may fit different projects.

The electric current acts as the heating element of this process. Fusion Welding: The name suggests that they melt together two separate pieces of metal due to heat generated because of an exothermic reaction during the process. Depending on the filler material used, there are three different fusion welding processes which includes gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) and Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW). Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW): is known as tungsten inert gas or TIG welding. A non-consumable tungsten electrode is used along with an inert shielding gas like argon for preventing oxidation of hot tungsten electrodes.
There are different methods for welding different materials. Welding methods used often include arc welding, resistance welding, and induction heating, among others. With arc welding, metal parts are heated with an electric current so that something can weld together them. This process melts the metal filler inside the joint gap between two parts and fills it with molten metal. Electric arcs produce ionized gas particles that are heated to extremely high temperatures when an electric current passes through them.
Type of Welding
There are two types of welding processes: fusion and soldering.
Fusion welding is the process of melting two pieces of metal together. In order to do this, a filler metal or electrode wire may be added to enhance the weld. The filler may also serve as a structural element itself, running through the part and linking separate pieces together to make one continuous piece.
Shielded Metal Arc Welding
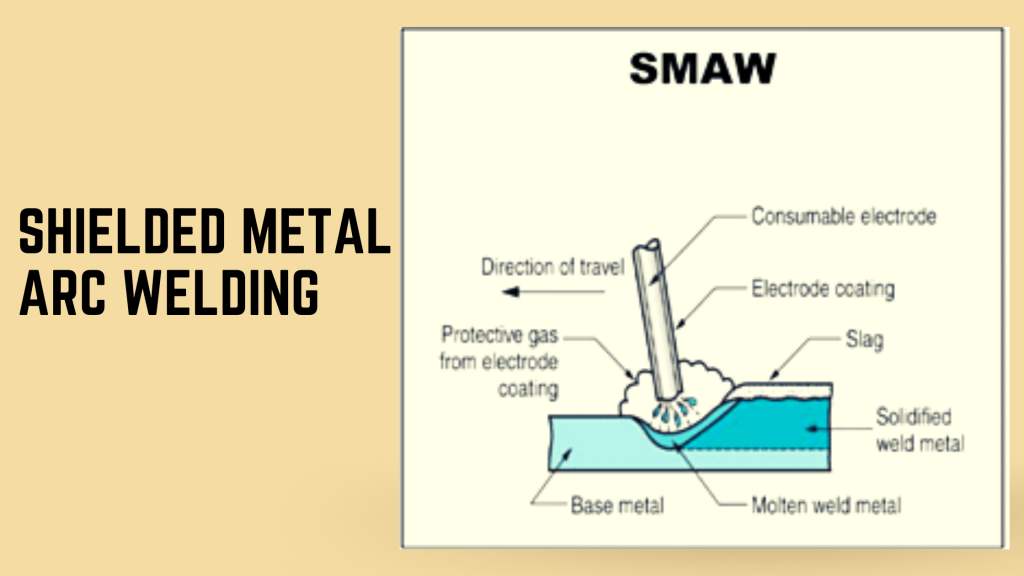
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), more commonly known as stick welding, uses an electric arc between a special tubular electrode and the material being welded in order to meet both metals at once. It’s most often used on steels from 1/8″ up to 3/4″. This method is used for flat, vertical, overhead or any other position that isn’t horizontal because it creates too large of a weld puddle when used in the flat position.
Gas Metal Arc Welding
Gas metal arc welding (GMAW) is also known as MIG welding because it uses an electric arc to heat the workpiece and melt the wire that’s fed into the weld puddle. The machine controls how much wire is fed, giving you more control over your weld than stick welding does.
MIG welding can be used with several types of filler materials like solid, flux-cored or cored wires all depending on what material you’re working with and its thickness. You can even use aluminium in this process which means you don’t need to switch to TIG if you’re planning to weld anything other than steel.
Shielded Flux-Cored Arc Welding
Shielded Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) is another form of GMAW. It’s a lot like MIG welding in the way that it has a shielding gas and filler material, however, instead of using a solid wire to make the weld, this process uses a hollow tube containing flux-cored wire. The flux helps protect the weld from contamination and oxidation which means you can use it inside or outside on all types of atmospheric conditions ranging from damp to wet.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) is similar to shielded flux-cored arc welding in that it also uses a shielding gas like argon or helium mix along with flux-cored wire as filler material. However, this method doesn’t use a tungsten electrode; therefore, you don’t need alternating current (AC) power like you do when TIG welding. This means you can use motors created for DCEP (Direct Current Electrode Positive) types of power sources to create the electric arc.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding
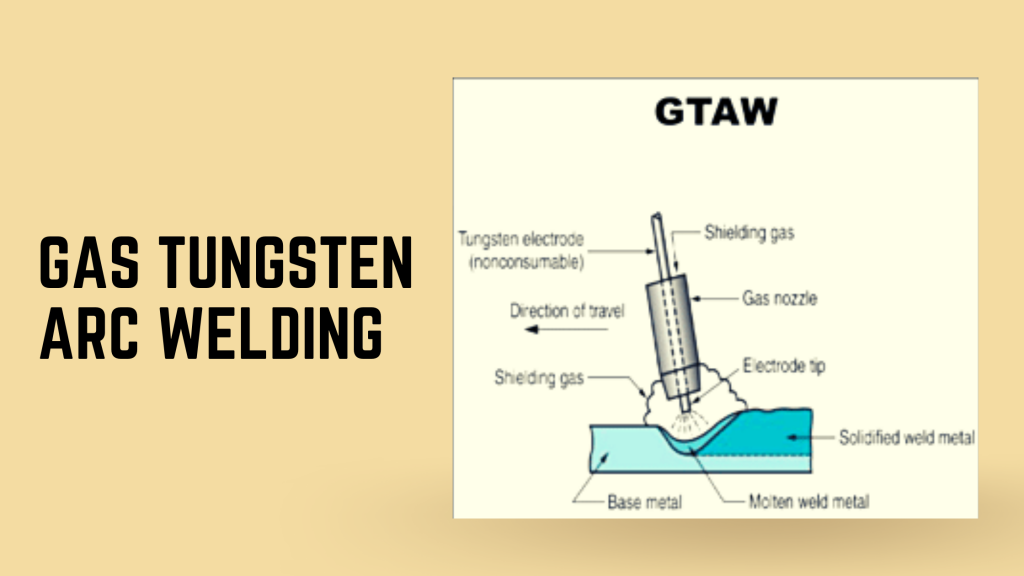
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), also known as TIG welding, provides the highest quality welds out of all arc welding methods because it uses an electric arc between a non-consumable tungsten electrode and the base metals being joined together. The filler material can be added to the weld puddle to enhance certain properties of the base metal, but it’s not necessary. It only works on materials that are electrically conductive and is mostly used for metal between 1/8″ and 1/4″ thick.
Soldering is any process that melts solder to join two metals together. Solder joints are usually strong but brittle, so they’re used for low-stress applications. Unlike fusion welding where one method works best, soldering methods vary depending on the metal being joined and other factors like temperature, pressure or flow rate.
The flux melts at a lower temperature than the metal itself which allows it to seep into cracks and crevices in order to loosen them up for removal later on. The liquid or paste can be applied to either wetted surfaces before heating, called “pre-tinning”, or to an already heated joint after it flows into the fissures.
Oxyacetylene welding and cutting is an older technique that’s still used today because it’s efficient and easy to learn. It works by heating the base metals until they become liquid and connect due to molecular attraction.
How does Welding Work?
Welding is a metal joining process that joins two pieces of metal. The welding area may vary in size, from items as small as a hand-held electronic component to a large steel structure such as a storage tank.

When metals are brought together under heat and pressure, they bond to form a weld. Although welding is not restricted to metalwork it is widely used in construction, shipbuilding and other industrial procedures, whether they are intended for use on land or underwater. Welding is the only way to join pieces of metal together, using heat and pressure to cause the pieces to bond. The basic principle is that metals are made up of atoms that are packed together in a structure that is either orderly or disordered. When a metal is heated it becomes less ordered and starts to take on a more chaotic structure. When this occurs, the metal can be “welded” together to form a bond with another piece of metal.
Common Joint Configurations
Welding is a fabrication or sculptural process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often done by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material (the weld pool) that cools to become a strong joint, with pressure sometimes used in conjunction with heat, or by itself, to produce the weld. It is often carried out in an enclosed space called a welding shop.
The welder is tasked with obtaining the correct posture and angle of approach to mitigate exposure to high-intensity radiation, to ensure the weld pool is of adequate size and shape, and to manipulate filler material so that a strong joint is formed. The welder must also maintain a clear vision of the weld area as it progresses to avoid missing areas and ensure adequate penetration.
Types of Welding Joints
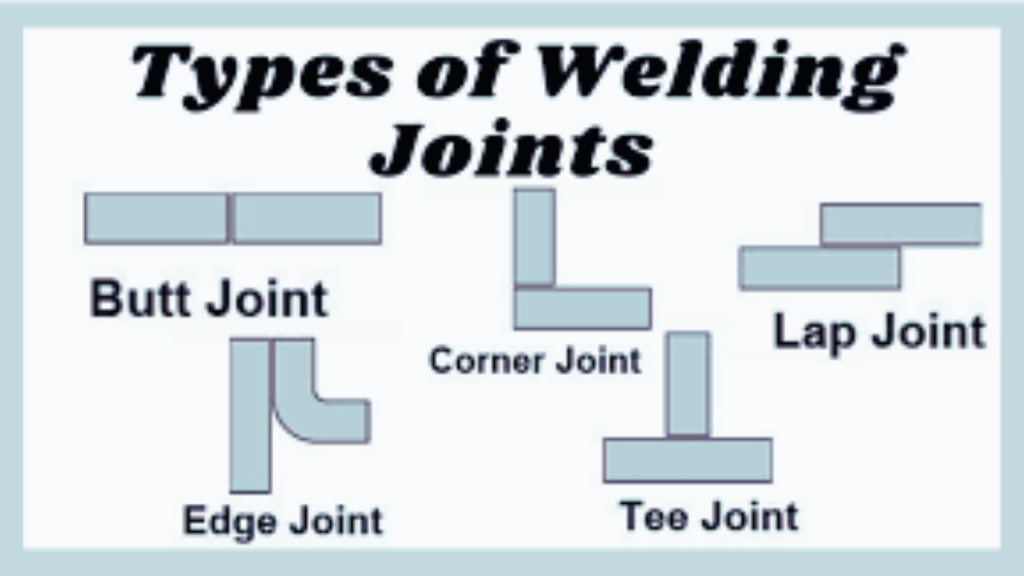
There are six common types of welding joints used today: fillet, butt, corner, tee (a form of lap), edge and projection. Each joint is formed by joining two pieces of metal together to form a complete piece. They are all produced in the same manner, but each has distinguishing characteristics.
There are three basic types of welding joints that are manufactured. The first is the butt joint which is made by bringing two pieces of material together at a right angle. Flange joints have the pieces welded together at a right angle and then curved around to form a circle or half of a circle. Lap joints are formed by overlapping two pieces of material at their edges. The piece with the greater thickness will be slightly curved around the thinner piece. The information which follows will describe the SIX types of welding joints in greater detail.
Butt Joints
A butt joint is formed by using two pieces of material that are cut to the same size. The edges are placed together and then welded together to form a straight line. There are two types of butt joints. If the pieces are edge to edge, it is called a square or solid weld. If the pieces are placed one on top of the other and welded, it is called a V-joint or keyhole weld.
Butt Joints are the easiest to understand because they are just that, two pieces of the same material being joined together to form a complete piece. A butt joint is the simplest type of joint to make, but the strength will depend on the metal being joined and how clean and smooth the cut surface is. If one of the pieces being joined has a slightly different thickness, it’s called a lap joint.
If the thickness is significantly different, it’s called a tee joint or step joint.
Corner joints
Corner joints are used when joining two pieces of material at right angles to each other. Butt joints are the same as far as joining two pieces of material together, but they are often used in different applications. Corner joints are most often used in applications where the two pieces will be joined at a 90-degree angle and they need to secure each other so neither piece will move. An example is to build a frame for an outdoor storage shed where two pieces of wood are nailed to each other at right angles, forming corners.
Fillet Joints
Fillet Joints are used to join two pieces of material together when a corner joint won’t work or will be less desirable for a particular application. A fillet joint is created by adding material to each of the two joining pieces, thus creating a smooth butt joint. A good example is the metal fitting on a water pipe that joins two or more pieces of pipe together before it goes into the floor, wall or ceiling. You can see that a fillet joint is just a butt joint with added material. The strength of the weld depends on the metal being used and how it is prepared for welding.
Lap Joints
A lap joint is formed by overlapping the pieces of metal and welding them together. The thickness of the thicker piece determines how much it will be curved around the smaller piece. The lap joint can be designed to make a V-shape or U-shape.
Lap Joints are used when two pieces of metal being joined have a large difference in thickness. A lap joint is the same as a butt joint, but because of the difference in thickness, one side will have a large area where another piece of metal is added. The strength of the weld is very dependent on how well it’s prepared for welding, but remember that the thicker side of the metal will be the most difficult to prepare for welding because the heat will have a tendency to warp the thicker side of the material. A good example of a lap joint is to take two pieces of plywood and put them together, standing vertically. A large difference in thickness can be seen between the two pieces and it’s of little use for building a shelf or some other project that needs the two pieces of wood perfectly flat.
Tee joints
Tee joints are sometimes classified as corner joints, but they’re used when pieces of metal need to be joined at right angles. Two pieces of the same type of metal are joined together at 90 degrees, making a corner joint. The pieces would be put together vertically or horizontally, depending on the application. A tee joint is slightly different because it creates a corner on both ends. Instead of having two pieces of metal at 90 degrees to each other, they form a tee on the end of the piece and this is where it gets its name.
Edge Joints
Edge Joints are used when two pieces of metal being joined have a large difference in thickness. A lap joint is the same as a butt joint, but because of the difference in thickness, one side will have a large area where another piece of metal is added. The strength of the weld is very dependent on how well it’s prepared for welding, but remember that the thicker side of the metal will be the most difficult to prepare for welding because the heat will have a tendency to warp the thicker side of the material. A good example of a lap joint is to take two pieces of plywood and put them together, standing vertically. A large difference in thickness can be seen between the two pieces and it’s of little use for building a shelf or some other project that needs the two pieces of wood perfectly flat.
Frequently Ask Questions (FAQs)
1. What Are The Basic Steps In Welding?
The basic steps in welding are:
- Clean the metal
- Apply flux to the work area
- Use a filler material that has a lower melting point
- Heat the metal to a molten state by using either a gas flame, electric arc or laser beam
- Allow the metal to cool down slowly
- What is the major difference between fusion welding and flame welding?
Fusion welding is carried out using electricity or gas flame. Flame welding does not use filler metal for joining the workpieces. It is a simpler process and the joint made is called a ‘butt joint’ as opposed to fusion welding which uses filler metal for making joints that are known as ‘groove joints’.
2. What Is The Mig Welding Process?
The metal inert gas (MIG) welding process was first introduced in the 1930s. This is an arc welding process in which the filler metal is fed by an inert gas (it can be either argon or helium) that protects the molten weld pool from atmospheric gases. The welded part is covered with a thin layer of slag that protects it from rusting.
3. What Is The Difference Between Welding And Adhesive Bonding?
In welding, the filler metal is heated to a molten state and then allowed to cool down slowly for joining the workpieces. In adhesive bonding, the workpieces are held together until the adhesive sets. The adhesive is a mixture of solvents and resins that have been activated by either heat or pressure.
Welding forms strong bonds but the bond formed in adhesive bonding is generally weaker than that of welding. However, adhesive bonding does not require high temperatures for joining the workpieces.
4. What Are The Different Types Of Welding Processes?
There are five major types of welding processes that are widely used throughout the world. These are:
MIG welding, TIG welding, stick welding, electron beam welding and laser beam welding. MIG welding, TIG welding and stick welding are arc welding processes whereas electron beam welding and laser beam welding are non-arc processes.
5. What are the 7 Basic Types of Welding?
- Energy Beam Welding (EBW)
- Atomic Hydrogen Welding (AHW)
- Gas Tungsten-Arc Welding.
- Plasma Arc Welding.
- Stick Welding – Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
- MIG Welding – Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
- Flux Welding – Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
- TIG Welding – Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
Benefits of Welding
Welding is a process that joins two pieces of metal together by heating the metal to a welding temperature and then pressing them together. The weld is created when the metals are at the same temperature and in a molten state. Welding has many benefits, including:
It is a durable and robust way to join metals together. – Welding is less expensive than other methods of joining metals. – Welding can be used to join various metals, including steel, aluminum, and brass. – Welding is a versatile process that can be used in many industries, including construction, manufacturing, and automotive. – Welding is a safe method of joining metals as long as it is done correctly by experienced workers. – Welds should always be inspected to make sure they are sound and robust. If the weld fails during use, it could injure or damage property. – Welding is a process that will continue to be used for many years and, as new technologies and procedures are developed, it will grow in popularity.
Welding has many benefits, including a durable and robust way to join metals together. Welding is less expensive than other methods of joining metals. Welding can join a variety of metals, including steel, aluminum, and brass. Welding is a versatile process used in many industries, including construction, manufacturing, and automotive. Welding is a safe method of joining metals as long as it is done correctly by experienced workers. Welds should always be inspected to make sure they are sound and robust. If the weld fails during use, it could injure or damage property. Welding is a process that will continue to be used for many years and, as new technologies and procedures are developed, it will grow in popularity.
- It is a durable and robust way to join metals together.
- Welding is less expensive than other methods of joining metals.
- Welding can join a variety of metals, including steel, aluminum, and brass.
- Welding is a versatile process used in many industries, including construction, manufacturing, and automotive.
- Welding is a safe process when done correctly.
Welding Equipment
Welding equipment is an essential part of the welding process. There are a variety of different types of welding equipment, including:
Welding machines – Welding torches – Welding rods – Safety gear
Welding machines are used to create the weld. They come in various sizes and can be powered by gas, electricity, or a diesel engine. Welding torches are used to heat the metals to be welded. They come in various shapes and sizes, depending on the type of welding being done. Welding rods are used to create the weld. They come in multiple sizes and shapes, depending on the welding type. Safety gear is also an essential part of the welding process. Welders must wear protective clothing and safety glasses to protect themselves from burns and sparks while working with hot metals.
Welding equipment is an essential part of the welding process. There are various types of welding equipment, including – Welding machines – Welding torches – Welding rods – Safety gear.
Welders use different types of welding machines to create the weld. These machines come in various sizes and can be powered by gas, electricity, or a diesel engine. Welding torches are used to heat the metals to be welded. They come in various shapes and sizes, depending on the type of welding being done. Welding rods are used to create the weld. They come in multiple sizes and shapes, depending on the welding type. Safety gear is also an essential part of the welding process. Welders must wear protective clothing and safety glasses to protect themselves from burns and sparks while working with hot metals.
Welders need to have the correct type of welding equipment for the kind of welding. In addition, they must always wear appropriate safety gear to protect themselves from injury.
Welding Machines
Welding machines are used to create the weld. They come in various sizes and can be powered by gas, electricity, or a diesel engine. Welding machines use different types of welding rods to create the weld. These rods come in various sizes and shapes, depending on the type of welding being done. In addition, they must always wear appropriate safety gear to protect themselves from injury.
Welders need to have the correct type of welding equipment for the kind of welding. In addition, they must always wear appropriate safety gear to protect themselves from injury.
Welding Rods
Welding rods are used to create the weld. They come in various sizes and shapes, depending on the type of welding being done. Welding rods use different types of welding machines to create the weld. These machines come in various sizes and can be powered by gas, electricity, or a diesel engine. In addition, they must always wear appropriate safety gear to protect themselves from injury.
Welders need to have the correct type of welding equipment for the kind of welding. In addition, they must always wear appropriate safety gear to protect themselves from injury.
Safety Gear
Welders must wear protective clothing and safety glasses to protect themselves from burns and sparks while working with hot metals. In addition, they must always wear appropriate safety gear to protect themselves from injury.
Welders need to have the correct type of welding equipment for the kind of welding. In addition, they must always wear appropriate safety gear to protect themselves from injury.
Welding Torches
Welders use different types of welding torches to create the weld. These torches come in various shapes and sizes, depending on the type of welding being done. Welding torches are used to heat the metals to be welded. They come in multiple shapes and sizes, depending on the welding type. In addition, they must always wear appropriate safety gear to protect themselves from injury.
How to Become a Welder
Welders are responsible for joining metals together by using heat and pressure. They use a variety of welding processes, including gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), flux-cored arc welding (FCAW), and submerged arc welding (SAW). Welders must be able to read and interpret welding blueprints and must be able to work safely in a variety of environments.
Welders typically have a high school diploma or equivalent. However, many welders also have an associate’s degree or a certification from a welding program. Welders must pass a certification exam to become certified.
Welders can find work in many industries, including construction, manufacturing, and transportation. They can also find a career in the military or the oil and gas industry. Certified welders can find work as welders, fabricators, layout technicians, and inspectors.
Welders typically earn a wage that is above the national median salary. The median pay for welders is $39,780 per year.
Certified welders can find work as welders, fabricators, layout technicians, and inspectors.
Welders typically earn a wage that is above the national median salary. The median pay for welders is $39,780 per year.
Welders must pass a certification exam to become certified.

It’s been years since I got into welding as a side hustle. It’s been so long since Doing All kinds of welds for business and pleasure as this is my hobby. Being in this field I have learned from hands-on-experience also came to know what gears work and what doesn’t. The Tig Welder is my own platform where I use to share my experience.






Leave a Reply